Introduction to Biomass Energy
Biomass is a renewable energy source made from organic materials. Bioenergy generated from biomass serves as a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, as it comes from renewable resources. It is often deemed. because it releases only the carbon that plants absorbed while growing. For example, trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and release the same amount when they die and decompose, thus maintaining a balanced carbon cycle without adding excess carbon to the atmosphere.
Biomass Overview
Biomass is a renewable energy source derived from organic materials. Bioenergy from biomass offers a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, as it originates from renewable resources. It is often regarded as “carbon neutral” because it releases only the carbon that plants absorbed during their growth. For example, when trees take in carbon dioxide, they release the same amount upon decay, thus maintaining a balanced carbon cycle without contributing excess carbon to the atmosphere.
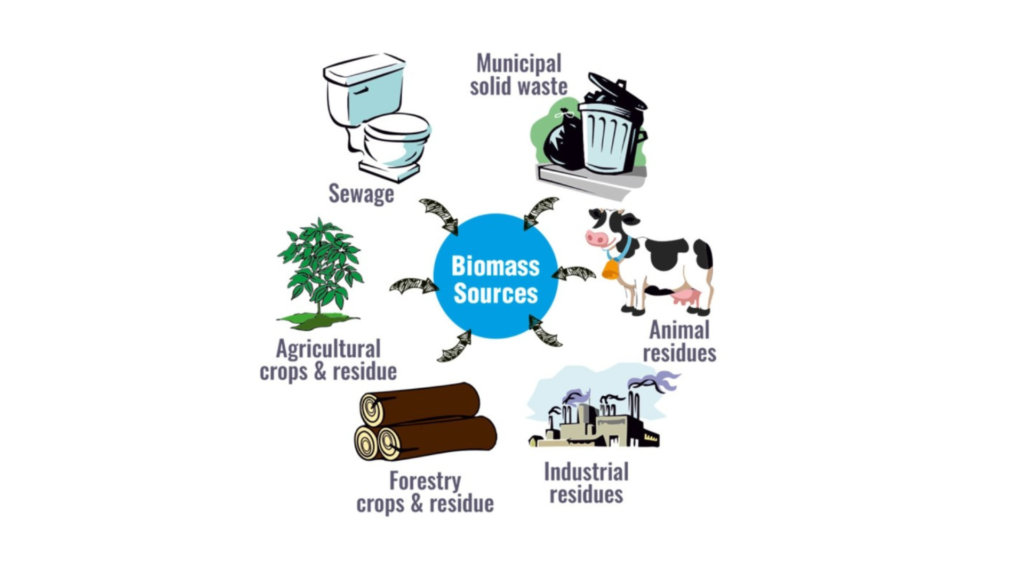
Forms of Biomass
Biomass comes in various forms, each with distinct applications:
Wood: Used extensively for heating in homes and industries, available as timber, chips, sawdust, or pellets.
Crops and Residues: Agricultural by-products like corn stalks and straw, as well as crops like corn and soybeans, are utilized for biofuel and energy generation.
Municipal Solid Waste (MSW): Household waste can be incinerated for energy or converted into fuel.
Animal Waste: Manure is transformed into biogas through anaerobic digestion for energy and heating.
Algae: Grown in controlled environments, algae serve as an efficient source for biodiesel.
Energy Crops: Crops such as switchgrass are cultivated specifically for energy production, providing biomass for heat and power generation.
Aquatic Plants: Plants like water hyacinths can be cultivated in water for energy production.
Advantages of Biomass
Biomass offers several benefits over fossil fuels:
Renewability: Biomass is sourced from organic materials, making it replenishable.
Carbon Neutrality: The carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by that absorbed during plant growth.
Waste Reduction: Biomass helps decrease landfill waste by converting organic materials into fuel.
Local Sourcing: Biomass can often be sourced locally, supporting local economies and reducing transportation costs.
Energy Security: It helps reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels, enhancing energy security.
Cost-effectiveness: While initial investment may be high, ongoing costs can be lower than those of fossil fuels.
Ecosystem Services: Biomass production can support environmental benefits like soil conservation and biodiversity.
Biomass Energy in India
Biomass energy is a key part of India’s renewable energy landscape, accounting for 32% of the country’s total energy consumption. As the second-largest producer of agricultural residues, India aims to achieve 175 GW of renewable energy capacity by 2022, with biomass expected to contribute around 10 GW.
Key sources of biomass in India include:
Agricultural Residues: Contributing about 65% of biomass energy resources, with potential generation of up to 18,000 MW from sources like rice straw and wheat straw.
Forest Residues: Account for about 18% of biomass energy consumption, with potential for generating up to 3,000 MW.
Municipal Solid Waste: Contributes around 5% of biomass energy usage, with a daily production of about 150,000 tons, potentially generating up to 5,000 MW.
Animal Waste: Cow dung and poultry litter can produce biogas, with an estimated potential of 12,000 MW.
Role of Biomass in Meeting Energy Demand
Biomass is crucial to India’s energy strategy, especially in rural areas where it is primarily used for cooking and heating. There is significant potential for large-scale applications in power generation to meet growing energy needs. Currently, over 70% of the population relies on traditional biomass fuels, presenting opportunities for expansion and diversification.
Biomass Energy by State
Maharashtra leads in biomass energy capacity, followed by Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and Tamil Nadu. Other states like Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Haryana, and Uttar Pradesh have notable biomass energy programs driven by resource availability and government support.
Biofuel Targets
The Indian government has set ambitious biofuel targets, aiming for 20% ethanol blending in petrol and 5% biodiesel blending in diesel by 2030. Initiatives like the National Biomass Cookstoves Initiative and the National Policy on Biofuels highlight the commitment to promoting biomass energy across sectors.
Environmental Benefits
Transitioning to cleaner biomass technologies can greatly benefit the environment. More efficient biomass stoves can reduce greenhouse gas emissions from cooking and heating by up to 70%. Modern biomass fuels, such as pellets, have lower moisture content and higher energy density, leading to more efficient combustion and reduced emissions. Additionally, industrial biomass facilities can incorporate technologies to minimize pollutants.


